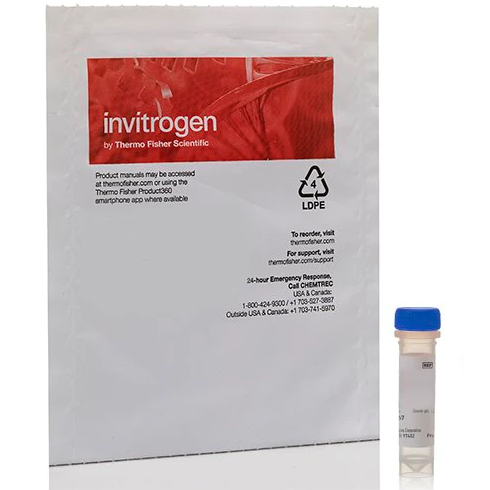
Invitrogen IL-17F Monoclonal Antibody (eBio18F10), PE, 100 µg, eBioscience™
On demandInvitrogen IL-17F Monoclonal Antibody (eBio18F10), PE, 100 µg, eBioscience™
The eBio18F10 antibody reacts with mouse IL-17F. IL-17F is a 37 kD homodimer of the IL-17 family and a signature Th17 marker. Of all the six IL-17 family members, IL-17F and IL-17A share the strongest homology (50% amino acid identity), and the two genes are located in the same chromosomal region. Recent studies have demonstrated coordinated regulation of IL-17A and IL-17F during Th17 differentiation. Expression of IL-17F and IL-17A has been detected in activated human peripheral blood lymphocytes, specifically by activated human CD4+ T cells. In addition to IL-17A, differentiated Th17 cells also produce IL-17F and IL-22 upon re-activation. Like IL-17A, IL-17F has been linked with inflammatory diseases. IL-17F and IL-17A expression has been observed in tissue samples from various autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, psoriasis, inflammatory bowel disease, and asthma. IL-17F treatment of airway epithelium, vein endothelial cells, and fibroblasts has been reported to induce expression of IL-6, IL-8, GRO-alpha, ENA-78, TGF-beta, MCP-1, G-CSF, GM-CSF, and ICAM-1.
Like IL-17A, IL-17F is a disulfide-linked homodimeric glycoprotein. The IL-17F homodimer includes a classical cysteine knot motif, which is found also in the TGF-beta, BMP, and NGF superfamilies. The presence of the cysteine knot motif suggested the possibility of a heterodimeric structure, as was reported for TGF-beta and inhibin/activin. Recent reports confirm that co-expression of IL-17F and IL-17A in HEK293 cells results in the formation of biologically active IL-17F/IL-17A heterodimers, in addition to the IL-17F homodimers and IL-17A homodimers. Moreover, activated human CD4+ T cells were found to produce the IL-17A/F heterodimer, along with the corresponding homodimers. In comparing the relative potency of IL-17A, IL-17F, and IL-17A/F, all three were found to induce GRO-alpha secretion; IL-17A was most potent, followed by IL-17A/F heterodimer, then IL-17F (100-fold lower than IL-17A). In the mouse, the IL-17A/F heterodimer (alone or in synergy with TNF-alpha) was found to regulate the expression of IL-6 and KC (mouse homolog of human GRO-alpha); this was found to be dependent on IL-17RA and TRAF6.
Features
- Excitation: 488-561 nm; Emission: 578 nm; Laser: Blue Laser, Green Laser, Yellow-Green Laser.
- Filtration: 0.2 µm post-manufacturing filtered.
- Recommended Isotype Control: Rat IgG2a kappa Isotype Control (eBR2a), PE, eBioscience™.
There are no specifications
There are no report
You May Also Like
Invitrogen 25 µg Rat IgG2a kappa Isotype Control (eBR2a), eFluor 506, eBioscience™
$ On demand
On demand
Invitrogen Rat IgG1 kappa Isotype Control (eBRG1), Brilliant Ultra Violet 805, 50 µg, eBioscience™
$ On demand
On demand
Invitrogen Rat IgM Isotype Control (eBRM), eFluor™ 660, 25 µg, eBioscience™
$ On demand
On demand
Invitrogen 50 µg Rat IgG2b kappa Isotype Control (eB149/10H5), PE, eBioscience™
$ On demand
On demand

Invitrogen IL-13 Monoclonal Antibody (eBio13A), Brilliant Ultra Violet 737, 100 µg, eBioscience™
$ On demand
On demand
Invitrogen CD54 (ICAM-1) Monoclonal Antibody (HA58), Functional Grade, 25 mg, eBioscience™
$ 10,212
On demand
Invitrogen CD16/CD32 Monoclonal Antibody (93), Unconjugated, 1 mg, eBioscience™
$ On demand